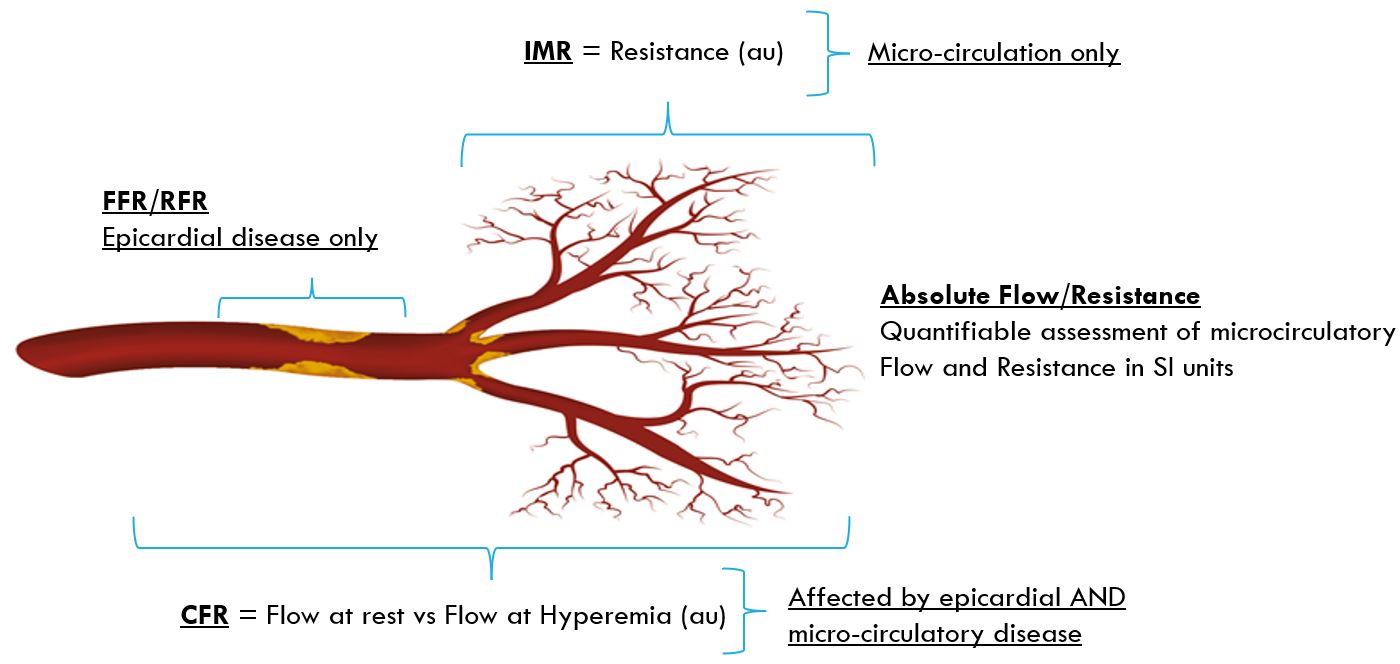
Methods for assessing microcirculation
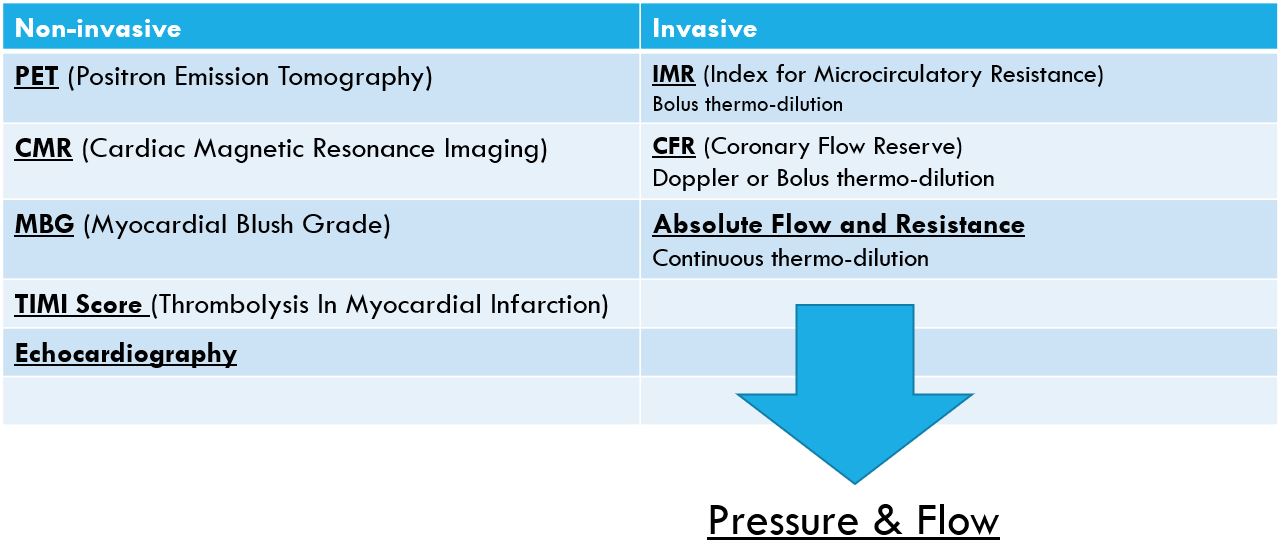
Measurement of coronary blood flow
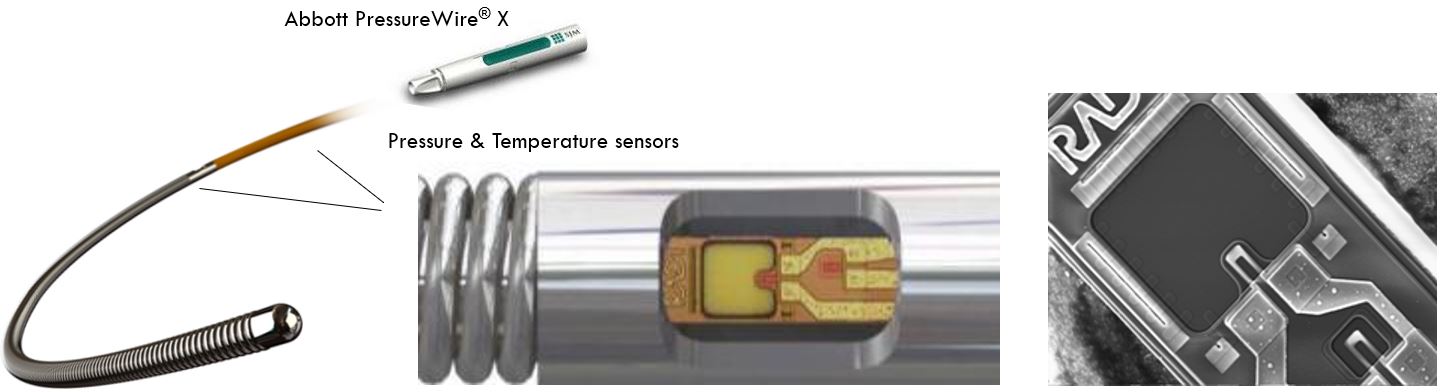
- Abbott PressureWire X: 175cm, ID 0.014” angioplasty guidewire with built in sensors
- Three sensors: Proximal temperature and distal Pressure and temperature
- Temperature sensors enable flow measurement through thermo-dilution
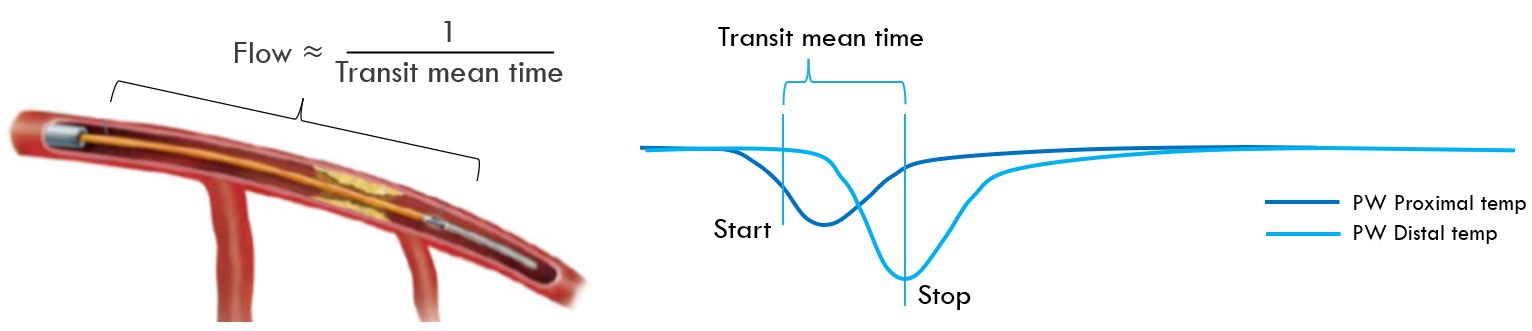
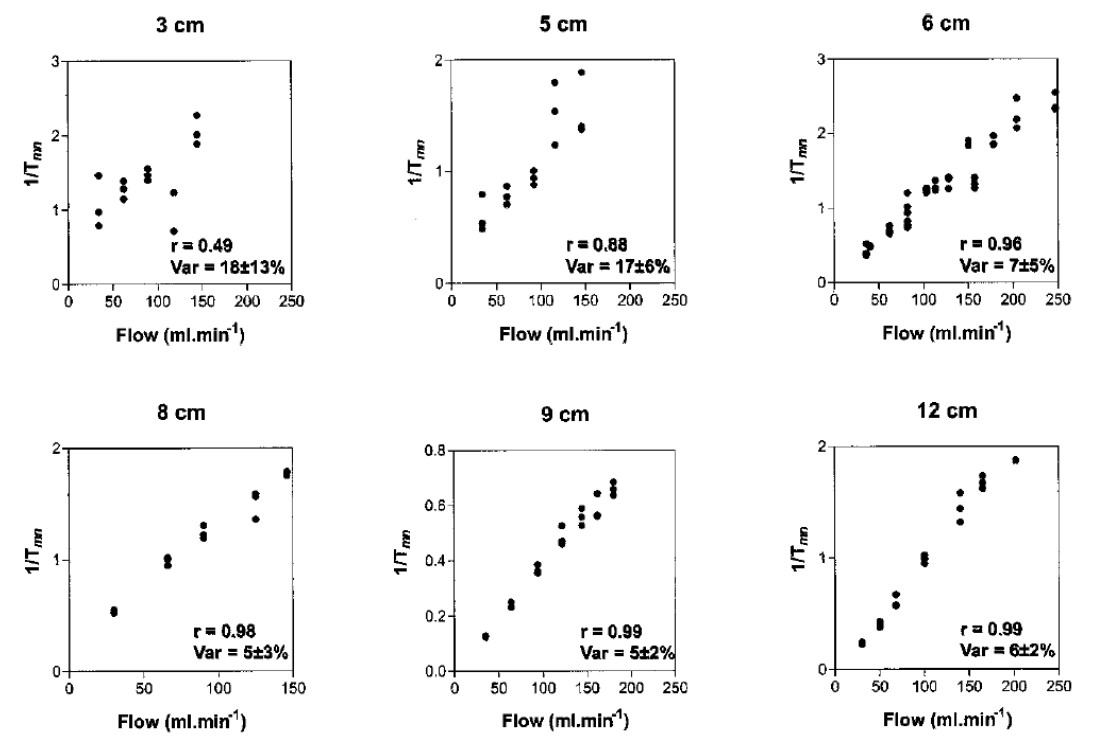
Flow by Bolus thermodilution
- Coronary blood flow is estimated inversely proportional to the time it takes for an injected bolus of room temperature saline to travel down the coronary artery
- By measuring the proximal and distal temperatures of the PressureWire the CoroFlow system can detect a bolus injection travelling down the artery and calculate the transit mean time: Tmn
Coronary Thermodilution to Assess Flow Reserve, Validation in Humans, Nico H.J. Pijls, Circulation. 2002;105:2482-2486
Flow by Bolus thermodilution
Coronary Thermodilution to Assess Flow Reserve Experimental Validation, Nico H.J. Pijls, Circulation. 2001;104:2003-2006.)
IMR-Index of microcirculatory resistance
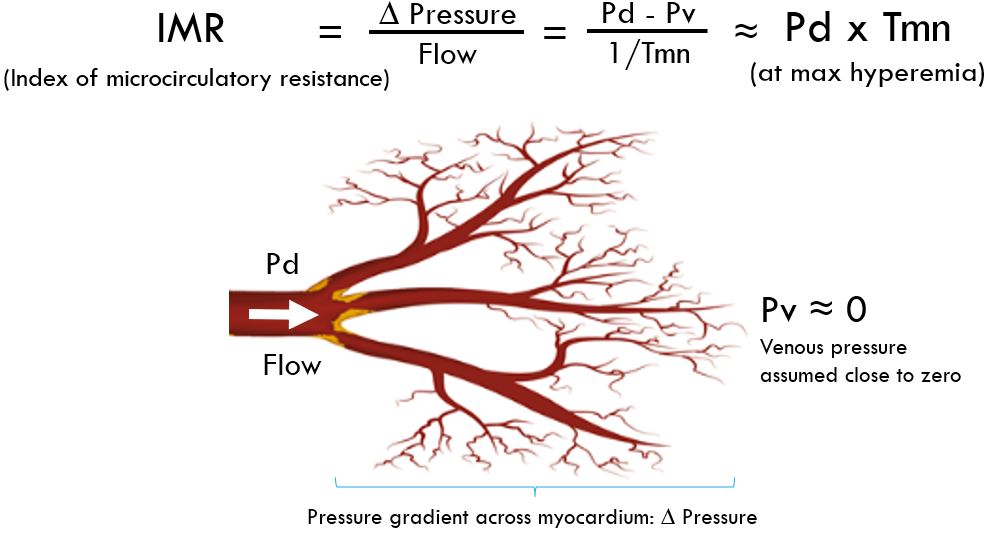
Index of Microcirculatory Resistance
Static Resistance at max hyperemia
IMR = Pd x Tmn
Normal value ≤25
Novel index for invasively assessing the coronary microcirculation. Fearon et al. Circulation. 2003;107:3129-3132
CFR-Coronary flow reserve
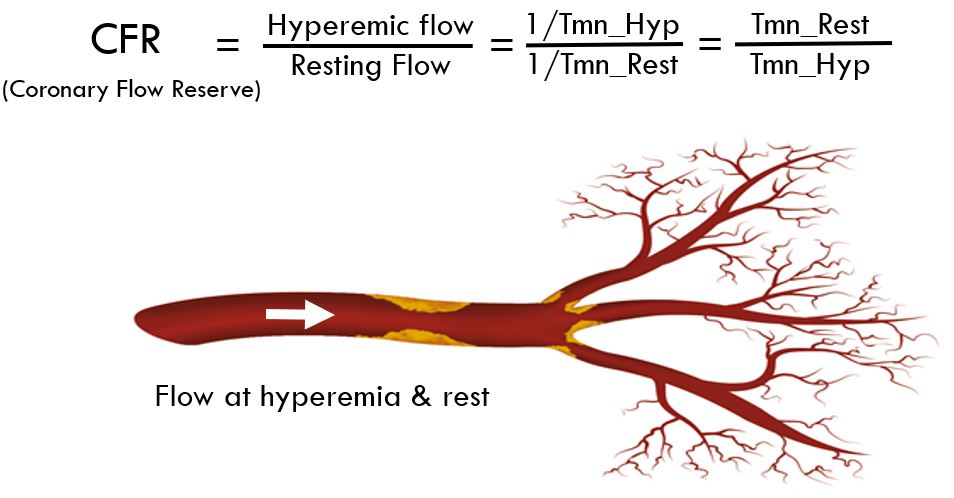
Coronary Flow Reserve
Dynamic Flow change from rest to hyperemia
CFR = Tmn_Rest / Tmn_Hyp
Normal value >2
Coronary Thermodilution to Assess Flow Reserve, Validation in Humans, Nico H.J. Pijls, Circulation. 2002;105:2482-2486
CFR by Bolus Thermo-Dilution vs doppler
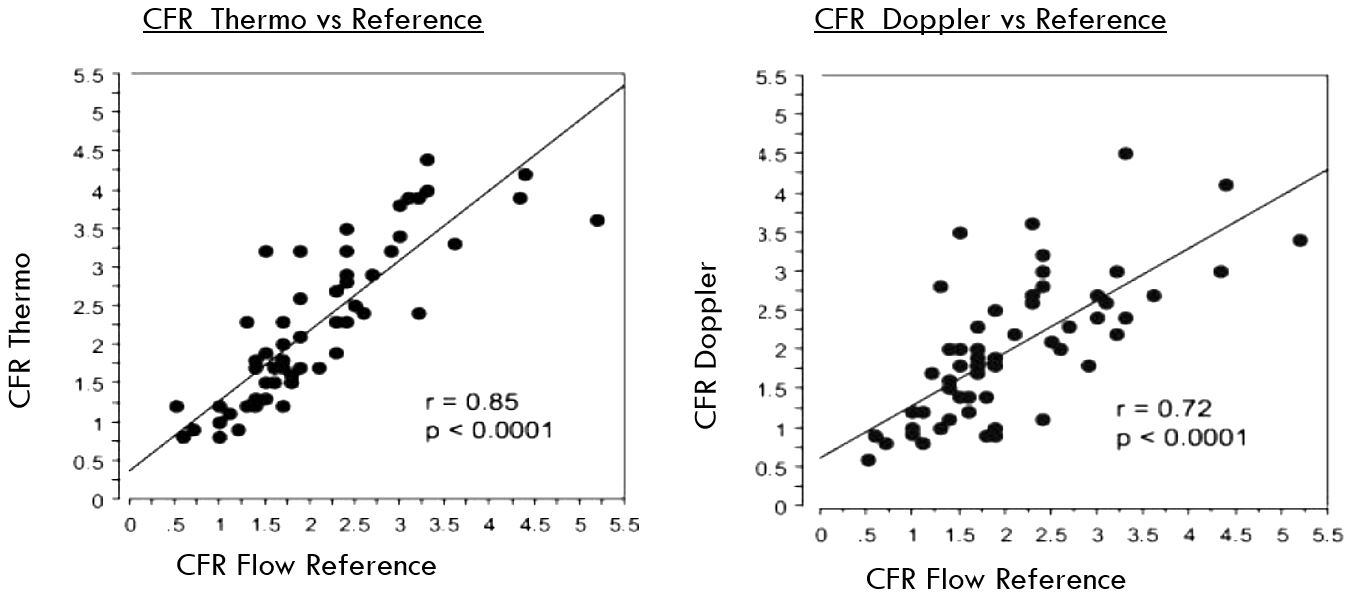
Comparison of Coronary Thermodilution and Doppler Velocity for Assessing Coronary Flow Reserve. William F. Fearon et al. Circulation. 2003;108:2198-2200